Behind every clinical trial, drug approval, or patient education resource, there is a medical writer turning complex science into clear communication.
Medical writers shape often technical data into something understandable and actionable. Whether it is a regulatory report for health authorities or a simple explainer for patients, the goal is the same: clarity, accuracy, and trust.
But what exactly does a medical writer do? And what skills, tools, and career paths define this growing field?
This guide breaks it all down. From the types of documents written to the ethics that underpin the profession, whether you’re exploring a new career or refining your skills, you will find what you need here.
Key Takeaways:
- What medical writing is and why it matters
- Common documents medical writers create (regulatory, clinical, educational)
- Core skills and training paths
- Ethical standards and compliance frameworks
- Career options in pharma, academia, and in international organizations
Key Concepts in Medical Writing
What is Medical Writing?
Medical writing is the practice of transforming complex scientific or clinical data into content that is clear, accurate, and tailored to a specific audience. It is more than writing; it is purposeful communication that supports decision-making in healthcare.
Medical writers bridge the gap between research and understanding. They take data from clinical trials, drug development, or peer-reviewed research and shape it into documents that guide actions and inform stakeholders.
Depending on the audience, this could include:
- Regulatory authorities reviewing drug applications
- Clinicians interpreting treatment data
- Patients seeking guidance on new therapies
- Academics preparing research for publication
The mission stays the same across every format: communicate clearly, ethically, and accurately.
For a deeper look at how this works in the pharmaceutical industry, read our article on medical writing for pharmaceutical companies.
Why It Matters
Clear communication ensures that science does not get lost in translation. Inaccurate, unclear, or biased writing can delay drug approvals, misinform patients, or create barriers in public health.
“Medical writing is essential for ensuring that the results of medical research are communicated clearly and accurately to a wide range of audiences,”
Dr. James Murtagh, medical communication expert
Without well-written protocols, study reports, consent forms, or journal articles, even the most promising scientific breakthroughs can stall. Worse, they might never reach the people they’re meant to help.
That’s why skilled medical writers are in high demand across:
- Pharmaceutical and biotech companies
- Contract Research Organizations (CROs)
- Academic and clinical research institutions
- Healthcare communication agencies
The Evolution of Medical Writing
Medical writing became a defined profession in the late 20th century as clinical research and regulatory processes grew more complex. With increasing demand for clear, structured communication, writers took on a critical role in drug development and healthcare delivery.
As pharmaceutical development accelerated, so did the need for specialists who could navigate clinical data, regulatory requirements, and scientific publication standards. Medical writers became part of interdisciplinary teams, working closely with researchers, clinicians, and regulatory affairs experts.
Today, the profession is broader than ever. Writers contribute to everything from global regulatory submissions to health blogs, slide decks, and digital patient education tools.
Digital platforms, AI-assisted writing, and global collaboration are shaping how content is created and delivered. Yet the purpose remains the same: to make medical information accurate, accessible, and meaningful.
Key Skills and Qualifications for Medical Writers
What it takes to write with authority, clarity, and trust.
Medical writing is not just about knowing science. It is about communicating science clearly, accurately, and with the right tone for each audience. Writers need a robust mix of technical knowledge, writing ability, and editorial judgment.
Core Skills Every Medical Writer Needs
- Scientific literacy
You should be able to understand clinical trial data, research methodology, and medical terminology. A background in life sciences, medicine, or public health is typically expected. - Clear, structured writing
Whether drafting a clinical study report or a patient brochure, your writing must be concise, consistent, and aligned with guidelines. - Attention to detail
Small errors in data, formatting, or terminology can lead to serious consequences in regulatory and scientific settings. - Audience awareness
Regulatory reviewers, clinicians, and patients each require different styles and formats. Adapting tone and depth is essential. - Critical thinking
Medical writers must interpret data, identify inconsistencies, and communicate findings in a balanced, ethical way. - Project management
Writers often manage multiple timelines and teams. Strong organization and version control are part of the job.
Educational Background
Most medical writers hold at least a bachelor’s degree in:
- Biology
- Pharmacology
- Nursing
- Public health
- Medicine
Advanced degrees (MSc, PhD, PharmD, MD) are common in regulatory and publication writing roles, especially in niche therapeutic areas.
Certifications That Boost Credibility
While not required, certifications can improve your profile, especially when transitioning from academia or journalism:
- AMWA (American Medical Writers Association)
Offers specialized training and the Medical Writer Certified (MWC®) credential. - EMWA (European Medical Writers Association)
Known for its Professional Development Programme (PDP) with in-depth workshops. - ISMPP (International Society for Medical Publication Professionals)
Ideal for those working in scientific publications or medical affairs.
Tip: Consider highlighting certification achievements on your CV or LinkedIn to stand out.
The Process of Creating Medical Documents
How complex clinical data becomes clear, structured content.
Medical writing follows a well-defined process. Whether you’re working on a clinical study report, a regulatory submission, or a patient factsheet, the steps are designed to ensure accuracy, compliance, and clarity.
Ideal for new writers or teams building a structured workflow.
Here’s how most medical writing projects unfold:
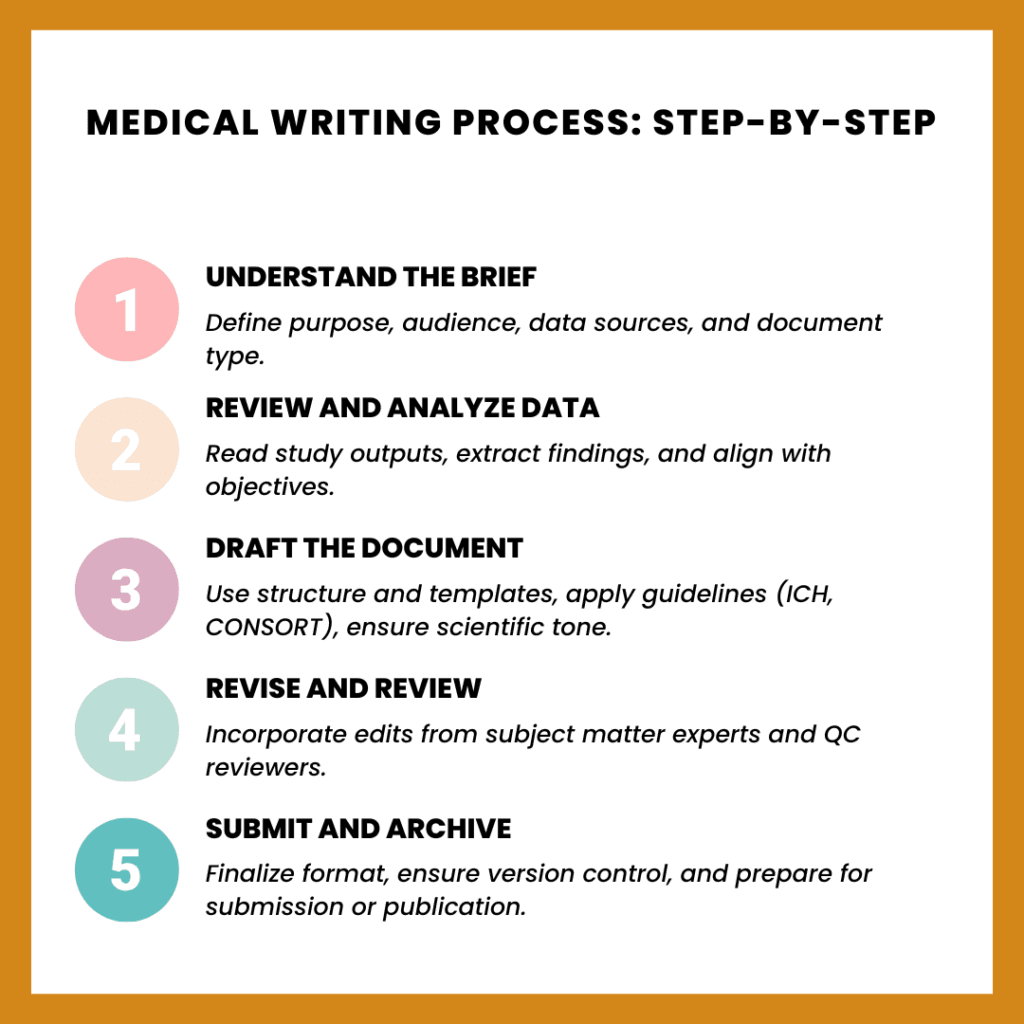
1. Understand the Brief
Before writing begins, it’s essential to clarify:
- The document’s purpose and audience
- Regulatory or publication requirements
- Key data sources and background materials
Writers may join kickoff meetings or review protocols, statistical reports, or previous versions of the document.
2. Review the Data
Writers interpret:
- Study results or raw clinical outputs
- Published literature or guidelines
- Supplementary materials from investigators or sponsors
This is where strong research and analytical skills come into play.
3. Draft the Document
Writers either work from templates or create a structure from scratch. Key principles include:
- Consistent terminology and tone
- Proper referencing (e.g., AMA, Vancouver style)
- Alignment with ICH, CONSORT, or journal guidelines
The draft is clear, objective, and ready for review.
4. Revise and Finalize
Revisions often involve input from:
- Medical reviewers
- Regulatory teams
- Subject matter experts
- Quality control reviewers
The writer coordinates edits, maintains consistency, and ensures the document meets standards.
5. Submit and Archive
Once approved, the document is formatted, submitted, and stored securely using:
- Internal portals for access and tracking
- Regulatory platforms (e.g., eCTD, CTIS)
- Document management systems (e.g., Veeva Vault)
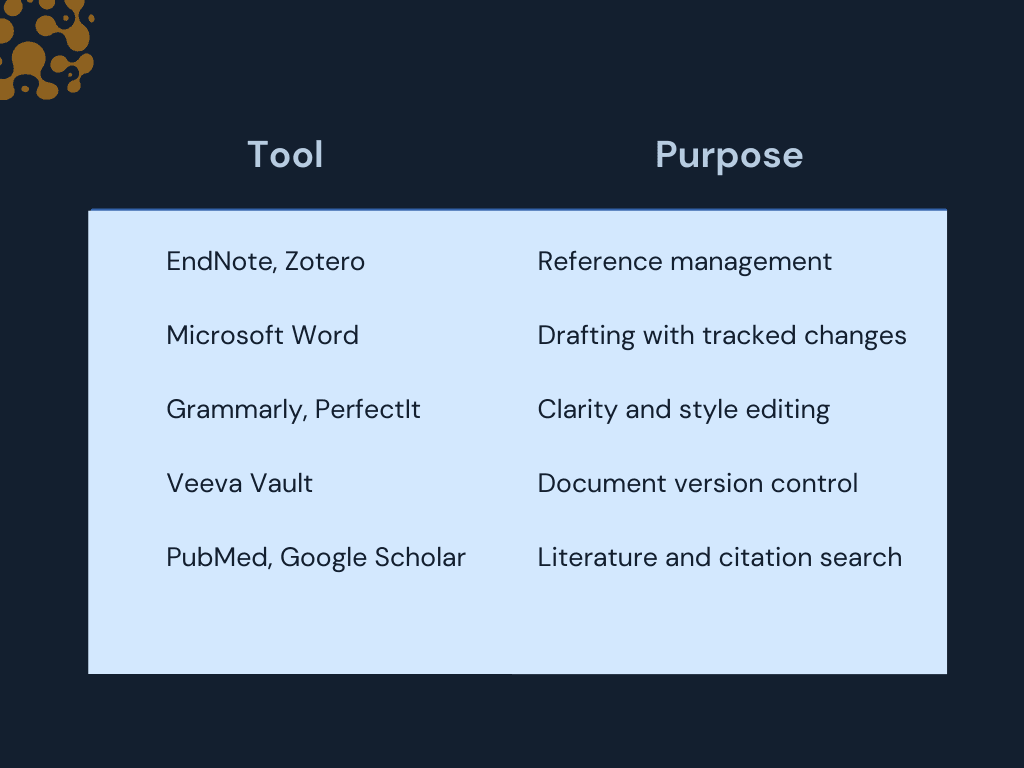
Common Tools Used by Medical Writers
Medical writers rely on a mix of research, editing, and collaboration tools. Here’s a quick overview of the most commonly used platforms in the profession.
Ethical Considerations in Medical Writing
Medical writers have a responsibility not just to inform, but to protect the credibility of scientific communication. Ethics in this field goes beyond accuracy. It touches on transparency, patient privacy, and public trust.
1. Accuracy and Transparency
Writers must present data truthfully, avoiding selective reporting or “spinning” results. This includes:
- Describing study design and methodology clearly
- Reporting both positive and negative outcomes
- Maintaining objectivity in tone and content
Documents, especially for publication, are often collaborative. Writers should ensure:
- All contributors are credited appropriately
- Ghostwriting is avoided
- Final drafts are approved by named authors
TIP: Follow the ICMJE and GPP3 guidelines to align with global standards.
3. Conflicts of Interest
Writers must disclose any financial or institutional affiliations that could affect objectivity. Full transparency helps readers evaluate the information with the right context.
4. Confidentiality and Privacy
Especially in regulatory or clinical documents, sensitive data must be protected:
- Patient information must be anonymized
- GDPR, HIPAA, and other privacy laws must be followed
- Confidentiality agreements should be honored, even after project completion
5. Ethics in Practice
Writers are expected to follow principles from organizations such as:
- ICMJE – International Committee of Medical Journal Editors
- GPP3 – Good Publication Practice
- COPE – Committee on Publication Ethics
- AMWA / EMWA – Promote ethical writing and transparency in communication
Upholding these standards isn’t just about compliance. It strengthens credibility, builds trust, and ensures that science serves its true purpose.
Types of Medical Writing Services
One profession, many formats, tailored to audience and purpose.
Medical writing is not one size-fits-all. Writers produce a range of documents depending on who they’re writing for regulators, clinicians, patients, or the public. Each type has its own tone, structure, and objective.
Medical writing spans several distinct formats, each tailored to specific audiences and objectives. Here’s a simplified breakdown of the main categories:
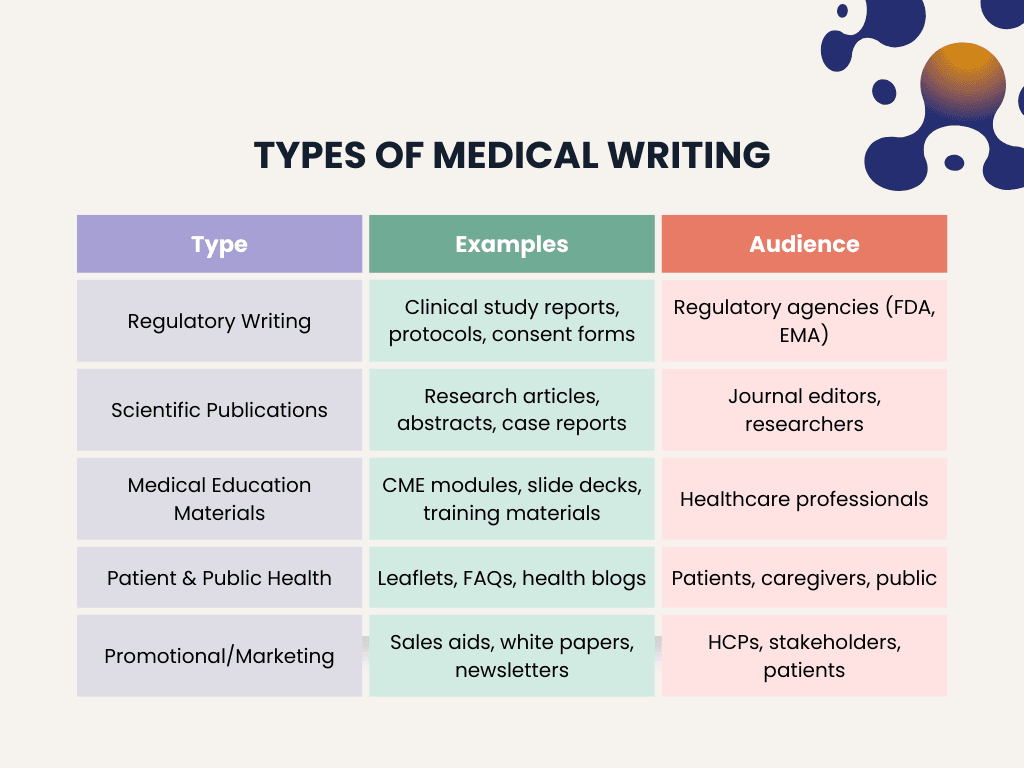
1. Regulatory Writing
Focused on documents submitted to health authorities for drug or device approvals.
Examples:
- Clinical Study Reports (CSRs)
- Investigator’s Brochures
- Protocols and Informed Consent Forms
- Product Information Leaflets (SmPCs)
Audience: Regulatory agencies like the FDA or EMA
Tone: Formal, factual, and compliant
Special skills: Familiarity with ICH guidelines and medical regulations
2. Scientific Publications
Writers help researchers prepare materials for academic journals and medical conferences.
Examples:
- Research manuscripts
- Abstracts and posters
- Review articles and case reports
Audience: Researchers, journal editors, peer reviewers
Tone: Evidence-based, objective, and editorially sound
3. Medical Education Materials
Content designed to train healthcare professionals.
Examples:
- CME modules
- Training slide decks
- Clinical guidelines and summaries
Audience: Physicians, nurses, healthcare staff
Tone: Instructional and informative
4. Patient and Public Health Writing
Designed to communicate clearly with non-specialist audiences.
Examples:
- Patient information leaflets
- Website content
- Health brochures and FAQs
Audience: General public, patients, caregivers
Tone: Empathetic, plain language, supportive
5. Promotional and Marketing Content
Supports healthcare marketing while staying compliant with ethical standards.
Examples:
- Sales aids and product monographs
- Branded blog posts
- Press releases and newsletters
Audience: Healthcare providers, buyers, and sometimes patients
Tone: Persuasive but evidence-based
The Impact of Digital Technology
How digital tools have reshaped the role of the medical writer.
Today’s medical writers work in a fast-moving digital ecosystem. Tools and platforms have transformed how content is researched, created, reviewed, and delivered.
Smarter Research and Referencing
Writers can now access up-to-date literature in seconds. Common tools include:
- PubMed and Google Scholar for sourcing publications
- EndNote and Zotero for managing references and citations
- PDF annotators for reviewing large volumes of material efficiently
Real-Time Collaboration
Many projects involve cross-functional teams working across time zones. Writers collaborate using:
- Microsoft Word with tracked changes for drafting
- Teams, Zoom, or Slack for communication
- Veeva Vault or SharePoint for version control and compliance
Enhanced Review and Editing
Automation supports quality without replacing human judgment.
- Grammarly and PerfectIt help ensure language clarity and consistency
- Style guides and custom dictionaries maintain brand and regulatory tone
- Formatting tools streamline structured document creation
Adapting for Digital Publishing
Medical writing is no longer limited to print or static PDFs. Writers may now need to:
- Prepare content for websites, apps, or open-access journals
- Develop plain-language summaries or visual abstracts
- Ensure materials are accessible and mobile-friendly
Writers who embrace digital tools gain an edge in efficiency and versatility, but clarity and ethical responsibility remain at the core of the craft.
Challenges Facing Medical Writers
The realities behind the work.
Medical writing is rewarding, but it comes with real pressures. Writers must balance accuracy, timelines, stakeholder input, and evolving standards all while keeping their audience in mind.
Keeping Up with Guidelines
Regulatory and journal requirements are constantly changing. Writers must stay current with:
- ICH updates
- EMA and FDA submission standards
- Journal-specific formatting and ethics policies
Falling behind can delay submissions or result in rework.
Balancing Clarity with Detail
Too much technical jargon can confuse readers, while oversimplifying can misrepresent the science. Writers must walk a fine line, especially when adapting content for multiple audiences.
Managing Feedback Loops
Documents often go through several rounds of review. Feedback can be:
- Conflicting across stakeholders
- Delivered under time pressure
- Based on personal writing preferences
Maintaining consistency and scientific accuracy during revisions is a key skill.
Tight Timelines
Medical writers often work within compressed schedules. They may face:
- Last-minute changes
- Late data delivery
- Regulatory submission deadlines
Time management and communication are critical for success.
Working Across Cultures and Teams
In global projects, writers must:
- Align tone and terminology across regions
- Respect cultural nuances
- Coordinate with remote teams in different time zones
Emotional Weight
Some projects involve sensitive topics such as terminal illness or treatment failure. Writers must stay objective while remaining respectful and empathetic. These challenges are part of what makes medical writing a respected, high-impact profession. Writers who succeed bring more than writing skill they bring resilience, adaptability, and sharp critical thinking.
Career Opportunities in Medical Writing
Where the work happens and how to get started.
Medical writing is one of the few science-based careers that combines communication, healthcare knowledge, and flexibility. With growing demand for accurate health information, the field offers a variety of roles and paths.
Where Medical Writers Work
- Pharmaceutical and biotech companies – Writing regulatory documents, drug dossiers, and product labels
- Contract Research Organizations (CROs) – Supporting clinical trials through protocols, reports, and submissions
- Medical communications agencies – Developing educational content, symposia materials, and digital campaigns
- Academic institutions – Assisting with manuscripts, grants, and ethics board documents
- Hospitals and NGOs – Creating patient education materials and public health content
Job Titles You Might See
- Medical Writer
- Regulatory Writer
- Scientific Writer
- Publication Specialist
- Medical Communications Associate
Some roles are highly specialized (e.g., oncology, rare diseases), while others cover a broad range of content types.
Freelance and Remote Options
Many medical writers work as independent consultants or remote contractors. This path offers:
- Project-based flexibility
- International client opportunities
- Options to specialize in areas like rare diseases or CME content
Freelancers typically set their own schedules and rates but must manage workflow and business development independently.
Breaking Into the Field
People enter medical writing from:
- Clinical backgrounds (nursing, pharmacy, medicine)
- Scientific research
- Journalism or health communication
- Graduate programs in biomedical sciences
Entry-level experience may come from:
- Internships with agencies or CROs
- Volunteering to help researchers publish manuscripts
- Blogging or writing for open-access platforms
- Earning certificates from AMWA, EMWA, or ISMPP
Improving Your Skills
Because great medical writers are always learning.
Medical writing is a field where ongoing development matters. Scientific knowledge evolves, standards change, and technology updates fast. Staying relevant means committing to continuous improvement.
1. Strengthen Your Scientific Foundation
- Follow journals in your therapeutic area
- Subscribe to updates from the FDA, EMA, or WHO
- Attend webinars and clinical trial briefings
Writers with up-to-date domain knowledge add more value especially in specialized fields like oncology or infectious disease.
2. Sharpen Your Writing and Editing
- Practice structured, template-based writing
- Learn to edit for clarity, consistency, and tone
- Understand submission formats and documentation standards
Use tools like Grammarly, PerfectIt, or built-in style guides to refine your work.
3. Get Comfortable with the Tools
- EndNote / Zotero – Manage references
- Veeva Vault / SharePoint – Version control and compliance
- Microsoft Word with tracked changes – Collaborative editing
Digital fluency helps you work faster and collaborate more effectively.
4. Earn Relevant Certifications
- AMWA – For North America-focused medical writing
- EMWA – For those in Europe or working with EU clients
- ISMPP – If you’re focused on publication or medical affairs
These certifications show professionalism and help build credibility especially for freelancers or career changers.
5. Build a Portfolio and Ask for Feedback
Keep a record of writing samples that show your range (regulatory, educational, public-facing). If under NDA, create anonymized mock samples. Ask for feedback from clients, editors, or peers. Even a single suggestion can reveal patterns or opportunities for growth.
6. Join the Community
Connect with other writers to learn, share, and stay motivated:
- LinkedIn groups (AMWA, EMWA)
- Peer writing groups or critique circles
- Conferences, forums, or webinars
You don’t have to learn everything on your own. A strong network accelerates your growth.
The Future of Medical Writing
Evolving tools, growing roles, and expanding influence.
While the core of medical writing remains the same clear and ethical communication the landscape around it is changing rapidly. Writers today need to adapt to digital platforms, specialized content, and global collaboration.
Digital-First Mindset
Medical content is no longer written for print alone. Writers now create for:
- Websites, portals, and mobile apps
- Open-access journals with HTML/XML formatting
- Visual abstracts and interactive modules
Understanding how content is published and consumed helps writers stay relevant.
Growing Demand for Specialization
Therapeutic areas like oncology, rare diseases, and gene therapies require deep subject expertise. Writers with niche knowledge will have more opportunities and can command higher fees.
Remote and Global Collaboration
As more teams operate virtually, medical writers must:
- Align with regional regulations (FDA, EMA, MHRA)
- Respect cultural and language differences
- Use collaborative tools to work across time zones
Flexibility and digital coordination are now core skills.
Focus on Transparency and Accessibility
There is increasing demand for:
- Plain-language trial summaries for patients
- Open science and data sharing
- Public-friendly science communication
Writers play a key role in bridging technical content with real-world understanding.
Technology Will Support, Not Replace
While AI tools may assist with formatting or grammar, the value of a skilled writer lies in:
- Judgment
- Ethical interpretation
- Audience insight
- Narrative flow
Those who combine scientific credibility with communication savvy will thrive.
Conclusion
Medical writing is more than a career. It is a responsibility to ensure that complex information reaches the right people, in the right way, at the right time.
From clinical trial documentation to patient education, the work of a medical writer can influence treatment outcomes, regulatory approval, and public understanding. The tools may change, but the goal stays the same: to make science accessible, trustworthy, and useful.
FAQs
How do I become a medical writer?
To become a medical writer, start with a background in life sciences, healthcare, or science communication. From there, gain experience in writing through internships, courses, or freelance work and consider certifications from AMWA or EMWA to strengthen your credibility. A strong portfolio of writing samples is often more valuable than formal training alone.
What types of documents do medical writers create?
- Clinical study reports (CSRs)
- Regulatory submissions
- Journal manuscripts
- Continuing medical education (CME) content
- Patient education materials
- Medical marketing collateral
Can I pursue a career in medical writing with a background in journalism or non-science fields?
Yes, while a background in science is helpful, it is not mandatory. Strong writing skills, curiosity, and a commitment to understanding complex topics can open doors. Many professionals transition from journalism, education, or technical writing. Taking a short course in medical writing or volunteering on small projects can help you get started.
What is an example of medical writing?
Examples of medical writing include a clinical trial summary written for a regulatory agency, a research article in a medical journal, a patient information leaflet explaining treatment side effects, or a white paper on a new healthcare technology. Each serves a specific audience and purpose
What should a medical writing resume include?
- Software skills (Word, EndNote, reference managers)
- Relevant academic background (science or writing)
- Writing samples or publications
- Familiarity with guidelines like ICH, GPP3, or CONSORT
- Experience working with multidisciplinary teams or reviewing data
Is medical writing a good career?
Medical writing is a fulfilling and in-demand career that offers intellectual challenge, flexibility (including freelance and remote work), and a chance to contribute meaningfully to healthcare. It is especially rewarding for those who enjoy continuous learning and clear communication.
How do I get into medical writing in the UK or Europe?
Start by joining organizations like EMWA, attending conferences, or taking their Professional Development Programme (PDP). Many UK and EU-based agencies offer internships, entry-level positions, or contract roles that provide valuable experience.
Looking for Expertise in Medical Writing?
Unlock the potential of high-quality medical writing with our team of experts at Epitech Research. We are dedicated to helping you communicate complex medical information clearly and accurately, ensuring that your documents meet the highest standards of precision and compliance. From clinical trial reports to regulatory submissions, our expertise ensures your success.
